The QS World University Rankings are a prestigious set of rankings that assess the performance and reputation of universities globally. Established in 2004 by Quacquarelli Symonds (QS), these rankings have become one of the most influential tools for students and educational institutions to gauge university
Ranking Methodology
The indicators used in the QS Asia University Rankings and their respective weightings are as follows:
- Academic Reputation (30%): This is assessed through a global survey of academics who identify leading universities in their fields. This survey is crucial for gauging the perceived quality of institutions within the academic community.
- Employer Reputation (10%): Based on feedback from employers regarding which universities produce high-quality graduates, this indicator reflects the employability of graduates from these institutions.
- Faculty-Student Ratio (20%): This metric evaluates the number of full-time academic staff relative to student enrollment, providing insights into the level of academic support and interaction students can expect.
- Citations per Paper (15%): Utilizing data from the Scopus database, this indicator measures research impact by assessing how often research papers published by an institution are cited.
- Papers per Faculty (15%): Also based on Scopus data, this metric assesses research productivity by calculating the number of research papers published per faculty member.
- Proportion of International Faculty (2.5%): This indicator measures the percentage of faculty members who are classified as international, reflecting the institution’s internationalization efforts.
- Proportion of International Students (2.5%): Similar to the previous indicator, this assesses the percentage of students who are international, indicating how attractive the university is to foreign students.
- Proportion of Inbound Exchange Students (2.5%): This metric evaluates the size of inbound exchange programs, highlighting how many students come to study at the institution from abroad.
- Proportion of Outbound Exchange Students (2.5%): This measures the size of outbound exchange programs, indicating how many students from the institution study abroad.
The combination of these indicators aims to provide a comprehensive view of each university’s performance across various dimensions, including academic quality, research output, and international engagement. The methodology was developed in consultation with regional experts to ensure it aligns with key educational priorities in Asia
quality
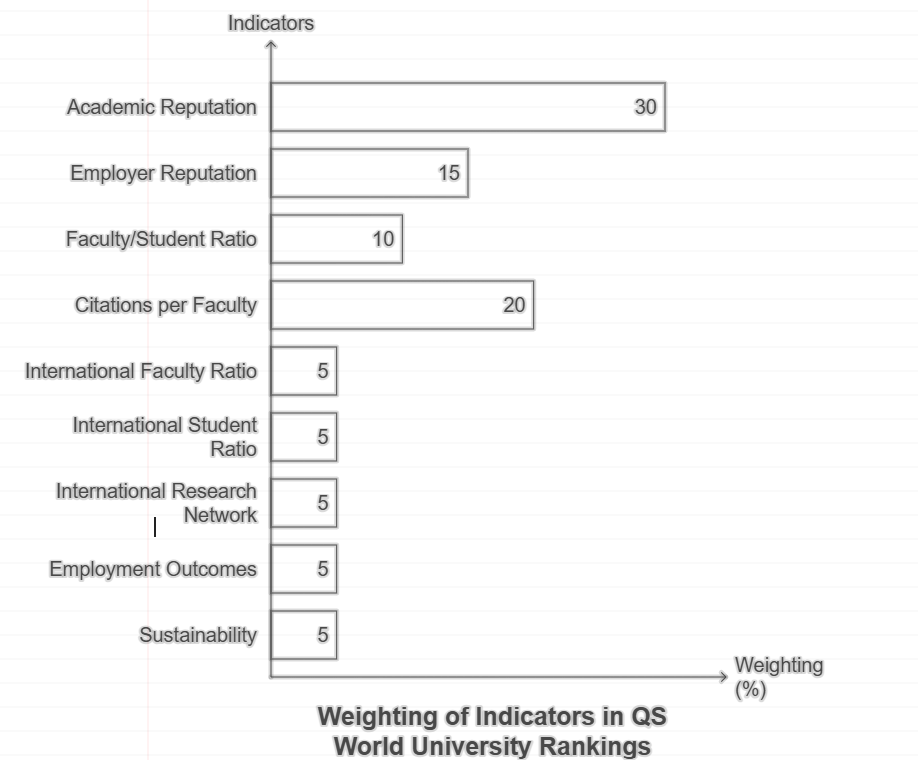
Weighting of Indicators in QS World University Rankings
The QS Asia University Rankings 2025 have been released, showcasing significant developments in higher education across Asia. India has notably surpassed China in terms of university representation, with 163 Indian universities making it onto the list, compared to 135 from China. This marks a substantial increase in India’s presence in the rankings, reflecting a growing emphasis on higher education quality and research output in the country.

Key Highlights
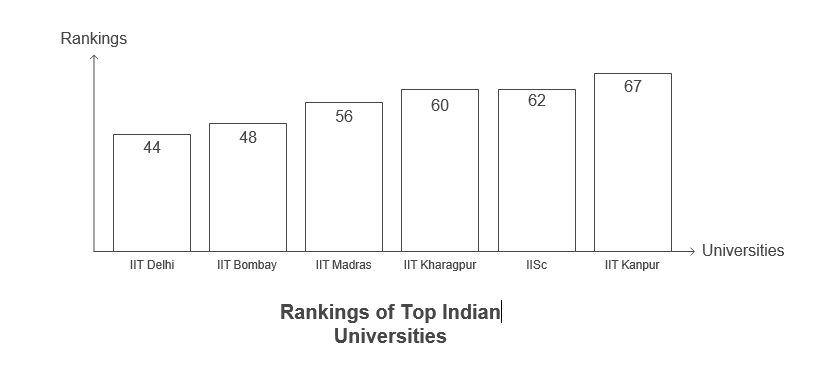
Top Indian Universities: The Indian Institute of Technology Delhi (IIT Delhi) leads Indian institutions at 44th place, followed closely by IIT Bombay at 48th and IIT Madras at 56th. Other notable mentions include:
- IIT Kharagpur – 60th
- Indian Institute of Science (IISc) – 62nd
- IIT Kanpur – 67th.
Overall Performance
Overall Performance: Among the Indian universities, 59 improved their rankings, while 51 declined, and 31 remained stable. Notably, Chandigarh University made a remarkable leap, rising by 29 places to rank 120th, indicating a strong upward trajectory.

The Bigger Picture
But what does this achievement really mean for India? It signifies more than just a numerical ranking; it reflects a broader narrative about the evolution of higher education in our country. As we witness an increasing number of universities making their mark on the Asian stage, it becomes clear that India is investing in its future.
The focus on research output, international collaboration, and employability is paving the way for a new generation of thinkers, innovators, and leaders.Moreover, this achievement comes at a time when the world is looking towards India as a hub for talent and innovation. The emphasis on quality education aligns with global trends that prioritize skill development and research capabilities. As Indian universities continue to climb the ranks, they not only elevate their own status but also enhance India’s reputation on the global academic front.
